When it comes to evaluating cross-platform frameworks, the biggest debate is between React Native and Ionic. The purpose of this article is to compare the performance, user experience, and many other topics of React Native vs Ionic.
React Native vs Ionic: Which Framework is best and Why?
The fun thing about working in the services industry is you get to interact with many different technologies. We will see how React Native and Ionic differ in terms of platforms for creating non-native apps.
There is usually some ambiguity about which platform I should use to develop my enterprise app – “What platform should I choose?”. Though it is generally very specific, there are still some general guidelines we can follow (or at least try!) to better decide.
Functionality of React Native vs Ionic
In order to fully explain the differences between React Native and Ionic and to show their differences, let us first examine how these frameworks work under the hood.
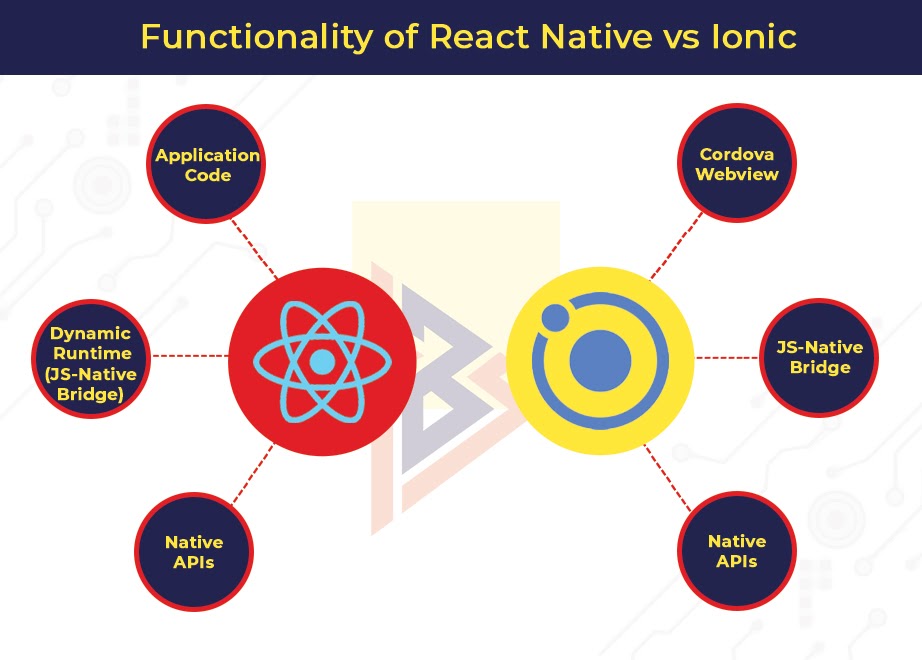
React Native: Functionality is based on dynamic runtime approach
React Native apps are developed using Javascript. Javascript code communicates with platforms (iOS, Android) through native platforms APIs that relay data calls and functions to a Javascript API that is mobile friendly. Both of these APIs connect via a bridge.
It is precisely because of this bridge that React native apps almost work like native apps!
Ionic: Functionality is based on WebView Wrapper
Ionic uses Cordova rather than React Native which relies on the dynamic runtime approach. Cordova relies on Webviews (UIWebView on iOS and WebView on Android) or chromeless browser views. In order to render a HTML/ CSS user interface, the WebView component uses a HTML layout engine (WebKit/ Blink).
To communicate with the native platform, Cordova uses a Javascript-native bridge. WebView can use native APIs as well as device features, such as cameras, with this method of accessing native APIs.
React Native vs Ionic: Comparison of Popularity
In order to begin, let’s look at React Native’s popularity versus Ionic’s. Developer survey results for 2020 are as follows:
- The SDKs of Ionic have been used by 86% of web developers to develop extensive applications in the past year, but only 16% of web developers have chosen React Native.
- There are 72% of developers using Ionic tools, libraries, and frameworks to build PWAs compared to 21% who select React Native.
- With 238+ version releases, Ionic has over 41,000 stars on Github, and over 13,300 projects have been forked. As opposed to React Native, which has 334.6+ versions with 198,000+ projects that fork constantly and 89.1k stars on Github.
The State of JS, which provides a 2019 overview of Javascript, indicates that the satisfaction ratio over user count is higher for React Native than Ionic. Most are still unaware of the benefits or the functionality of Ionic as it is still gaining popularity at the moment.
Winner:
React Native. It is evident that React Native has more popularity than Ionic.
Learning Curve Feasibility: React Native vs Ionic
In both frameworks, JS is at the core of their SDKs. Their similarities end there. With React Native’s basic flex layout, getting the necessary components style is simple. Only CSS knowledge is required. In addition to Axios for calling APIs, Redux with React, Flexbox, and ES6 are also some other prerequisites.
The installation of Cordova through Ionic is simpler than through npm commands. Ngcordova provides you with Angularjs extensions and services in a packed and powerful package. The greatest advantage of Ionic is its own online school, Ionic Academy, which offers lessons on different levels to make learning and building easier.
Winner: Ionic. The learning process is much easier and simpler.
Comparison of Stack Structure: React Native vs Ionic
Putting the frameworks into perspective from the point of view of a technology stack.
Stack structure of React Native
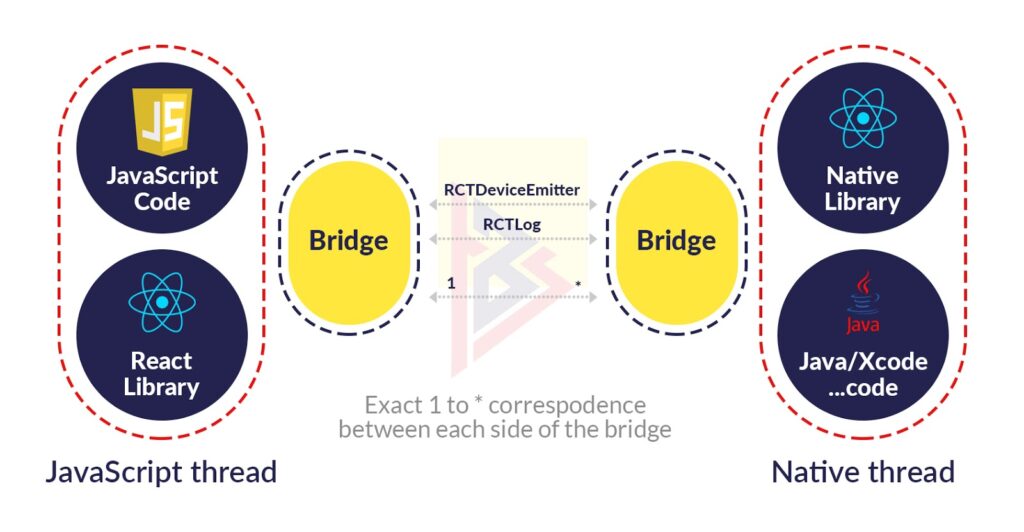
As mentioned earlier, communication between Javascript components and native components involves a bridge, which corresponds one to one between each component.
You can offload anything you can’t do with the Javascript part of React native to the native part if you can’t do it with the Javascript part. If that is the case, then you would build some components in React native and others as native components.
What is the difference between React Native and native? Develop Native applications with React Native for native platforms. Despite the fact that it can develop cross-platform applications, it cannot be considered hybrid since it does not share the ability to create a single codebase that can run on multiple platforms. React Native is also Core Native in some instances, in contrast to hybrid applications that use Cordova and HTML5.
Stack structure of Ionic
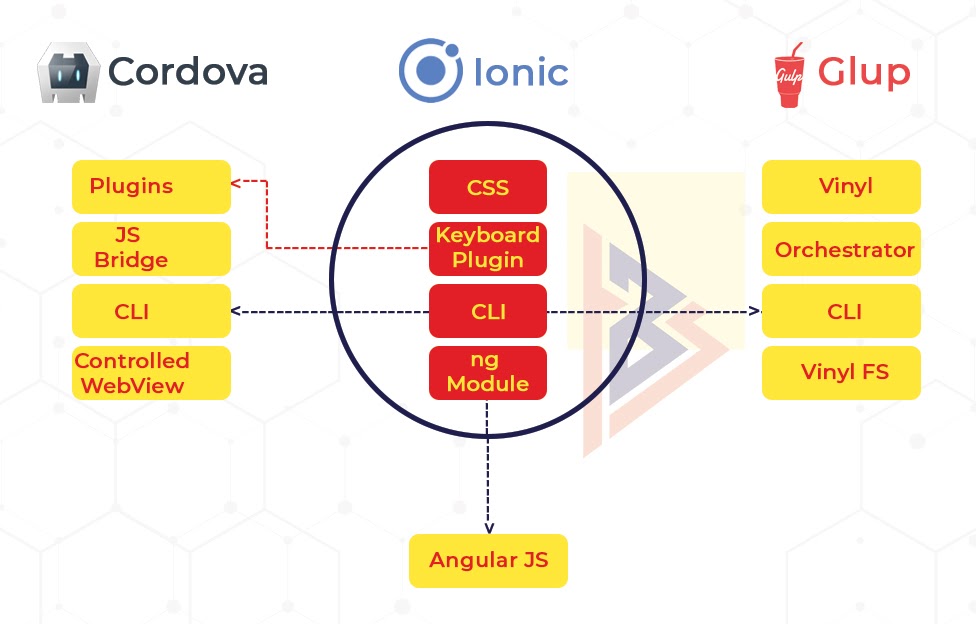
The ionic stack is comprised of three main layers:
- Ionic – User Interface Framework
It’s a framework that provides user interface components that aren’t available in the ecosystem of web applications.
Additionally, the Ionic framework comes with a command line tool that makes creating, developing, and deploying Ionic applications much easier.
- Angular – Web Application framework
For creating customized UI components, Ionic relies on AngularJS. Ionic can also leverage Angular’s framework capabilities, such as those associated with MVVM, MVC, and MVP.
- Cordova – Hybrid application framework
Cordova functions as a means of connecting WebView API with the native API of the device. Cordova’s main capability is to bridge the divide between these two technology stacks (WebView HTML and Native API).
Considering that Ionic uses native wrappers, such as Cordova or PhoneGap, you might wonder: is it native or hybrid? Hybrid frameworks such as Ionic are common. For clarity, let’s rewind and look at it from the perspective of the past. Use Ionic for Developing hybrid applications. To reach accessibility to native platform layers, Ionic reaches more towards the hybrid end of the spectrum. Also known as a hybrid framework, Ionic allows you to run native apps inside native shells.
Application Size
Expense Manager showed the following results regarding its app size comparison:
- Download Ionic Build 3.2MB
- The React native build is 8.5 MB (without using Proguard to reduce build size)
Winner: Ionic.
Ionic can create applications that are small in size when compared to React Native.
Securing Application Data
Using the secure storage cordova plugin, developers can ensure the security of their iOS app while working in Ionic. On Android, however, there must be a swipe lock or screen lock set in order for this to work.
Encryption in React Native: Developers have access to a wide range of third-party encryption libraries, including:
- React-native-keychain
- React-native-secure-storage and
- React-native-sensitive-info
Winner: React Native. Ionic and React Native provides a high level of security against application vulnerabilities; however, React Native provides the best options for securing applications.
Enterprise Compatibility
Ionic has been a favourable framework for developing hybrid/native apps and PWAs. It remains unclear whether React Native is officially recommended as a framework for Enterprises, although many renowned organizations such as Facebook, Airbnb, Wix have adopted it.
Winner: Ionic. Ionic is more enterprise-friendly than React Native.
Testing
React Native testing can be accomplished by using a variety of frameworks, including: ReactTestUtils, Jest, Jasmine, Mocha, XC Test, and Earl Grey, for testing iOS applications and automating iOS UI.
Ionic uses an end-to-end testing set up similar to that of Angular CLI. In this case, Ionic has the capability to use Karma for testing components, Protractor and Jasmine for unit testing and End-to-End testing.
Winner: Both React Native and Ionic. The testing for React Native covers units, automated tests, and Ionic covers component testing as well as end-to-end testing.
Debugging
The React Native debugger app, Console.log or Chrome developer tools can be used for debugging. Debugging is much easier with React Native applications. Here in debugging an app using native code can also be done using any editor such as XCode for iOS or Visual Studio for Android.
Also, debugging in Ionic is generally a simpler experience with tools like Chrome’s dev tools available to developers. ngCordova can be challenging, especially when a project uses hardware features.
Winner: Both React Native and Ionic. Use Chrome developer tools to debug both frameworks.
Continuous Integration & Continuous Deployment
Ionic builds, TestFlight, Codeship, Jenkins CI, Travis CI, Semaphore CI & CircleCI all allow for continuous integration and deployment pipeline implementation
Use the following CI-CD tools with React Native: Bitrise, Travis CI, CircleCI, and Jenkins CI
Winner: Both React Native and Ionic.
UX/UI Performance Comparison
In general, cross-platform and hybrid frameworks may have performance issues in terms of UX and UI. View the video of Tal Kol providing some insight into some of these challenges. A big challenge in working with Ionic is rendering your UI at 60fps. While libraries like React Native Interactable and Lottie by Airbnb have made it much easier to achieve 60 frames per second with React native, this is still a challenge.
Text inputs used in many applications such as the hitSlop prop, KeyboardAvoidingView, and TouchableNativeFeedback enable developers to improve user experience by providing more ways to enhance text input. With Ionic, you can create a simple hybrid application that runs on multiple platforms with a single codebase.
By eliminating separate native codebases for each platform, it reduces development and maintenance costs. Consequently, you can invest more time into improving the quality of the application and adding new features.
Winner: React Native.
ListView Scrolling comparison between React Native and Ionic
WebView, as mentioned earlier, wraps an application in an Ionic app. Due to this, Ionic, which renders through a WebView, is significantly slower than React Native, which compiles natively.
We will compare Ionic to React native performance using a very simple ListView example. While in Ionic, views are rendered within WebViews (HTML/CSS/Javascript) and not natively in React Native.
Winner: React Native. As a native application, React Native boasts superior rendering and performance over Ionic.
Developer Convince
To work efficiently with React Native, developers need some prior experience with React.js. When it comes to developing hybrid react native apps, some basic knowledge of native development (iOS/Android) is required in addition to javascript.
Ionic, a hybrid development platform based on WebViews, is somewhat similar in developer comfort to Web development.
Winner: Ionic. The Ionic framework makes it quite easy and feasible to create apps.
3rd party libraries
In case of Ionic, developers are fortunate for their convenience to search for any type of plugin from the bunch of libraries such as Apache/Cordova plugins, Ionic plugins from the marketplace, and Angular modules. With mind-boggling support from its community, React Native is also rich in its availability of 3rd party libraries or plugins.
Winner: Ionc.
Maintainability
With React native, any 3rd party library that you might use could get outdated or become incompatible with your updated codebase. Hence, maintainability remains a big issue.
As opposed to React Native, in Ionic you would only be required to maintain one single code (In React Native you would have to maintain both iOS and Android builds). However, the biggest challenge with the maintainability of Ionic apps is that the framework itself is undergoing continuous changes with frequent release cycles on Ionic and Cordova.
Winner: In this criteria, both React and Ionic are not winners. Maintenance of libraries in React Native and Ionic both is little inconvenient due to outdated updates or constant updates respectively.
OTA updates
In React Native, developers can deploy applications directly over-the-air to their devices with the help of Microsoft CodePush. It is possible to make changes to an Ionic app on demand with a feature called Ionic Deploy.
Winner: Ionic. The user can go back and forth between the latest and older versions of an application with Ionic.
IoT Integration
3rd party libraries are available to integrate IOT within a React Native app.
React-native-aws-native-device-shadows – This is a library for wrapping React Native components in SDN to hook up to AWS IoT.
In the future, IoT developers will be able to easily build frameworks and applications based on Ionic as it can be easily integrated with Bluetooth devices, Ibeacons and wireless sensors.
Winner: Ionic. Comparatively to React Native, it is easier to interface with IoT devices
Cost of development
According to the business perspective, both frameworks prove to be time and money savers. Ionic, however, is more affordable than React Native when comparing both frameworks. Due to the fact that Ionic gives you the option to develop hybrid applications that can run across multiple platforms by creating only one codebase.
Winner: Ionic. It’s a great way to save money, but might not be the best choice when the project requires hardcore native code.
Ionic 2 vs React Native
The functionality of Ionic 2 is based on Angular 2.x versions, one of the significant improvements made with it. The OnPush strategy is used by Ionic 2 components. According to the strategy, changes in the application are only detected when the input changes, rather than always automatically during execution. Application components are not rendered excessively in this way. During the build, your application is already optimized.
Angular 2.x is 110% faster than Angular 1.x at creating a data table using vanilla Javascript services. Thanks to Angular 2.x, Ionic 2 can significantly increase its performance. In this case, Ionic 2 is virtually equal to React Native in terms of performance. In spite of Ionic 2’s apparent performance, React Native still achieves higher standards when considering certain important factors, such as:
- A requirement for native callbacks in multiple formats
- It’s becoming more popular to use native UI designs
- Build Customise and Interactive transitions
- Customise Processing hardware for each platform unlike Cordova
Winner: React native. Ionic 2 and React Native have similar purposes, but they differ in regards to the requirements of your project.
Bottom Line (Conclusion)
What is the best framework to use for your app development requirements: React Native vs Ionic? I’ve included a list of points to consider when choosing a framework.
Choose React Native if:
- Using React Native, you already have an application or website.
- React is a specialty of your development team.
- You need to ensure your project is dependent on native platforms.
- Investing in your project and having enough time to develop it are important characteristics.
- The funds or budget you have are sufficient to cover a wide range of development expenses.
Choose Ionic, if:
- You are planning to launch your own startup with your new application idea.
- Your company’s growth depends on the development of your MVP.
- If you are considering competitions, you must take time into consideration.
- Getting the most value out of the digital market is similar to what your competitor proposes.
- A tight budget constrains your development expenses at the minimum.
For apps that revolve around video streaming, P2P marketplaces, social media or fitness functions, Ionic is a solid choice. With React Native, you can build an app that has higher performance, responsiveness, budget, and time requirements.
TechnoBrains has wide experience in mobile app development, we have a team of highly experienced developers who can turn your app idea into reality. Contact us to discuss your idea.
React Native vs Ionic — Tabular Comparison
FAQ
Which is better, Ionic or React Native?
In contrast to implementing native UI patterns for iOS and Android, Ionic React relies on cross-platform web technology instead of using platform controls directly. The performance of React Native may be higher because it uses a wide range of iOS and Android controls.
Which is better, native apps or Ionic framework?
Ionic gives you the ability to build iOS, Android, PWAs, desktop apps, and applications on any platform running the web using HTML/CSS/JS. Using React Native, you can build iOS and Android apps using the React JS framework, but rendering native UI elements at runtime.
What are the benefits of Ionic for Web?
It’s already incredible to have one code base that can be implemented in mobile apps as well as web applications, but the flexibility of CSS and responsive elements make it the perfect solution for building your next web app and PWA.
Does React have a future?
Its extra versatility and ease have made react development the future of web development. More than 1300 developers actively use ReactJS in development, with more than 94000 pages estimated to use ReactJS. AngularJS had many shortcomings that were overcome by ReactJS
In comparison to react native, what is better?
Social networks have made React one of the most popular front-end frameworks at the moment, with an active community. There are more stars on GitHub for Flutter than for React Native as of the time of writing. The popular commercial applications of both Flutter & React Native.








